Market Value with Charter
Introduction
VesselsValue has combined its Market Value (MV) and Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) models to produce Market Values with a Charter attached (MVWC).
Vessels are often sold with charters attached, which can have a significant impact on the price achieved. The MVWC gives the estimated sale price a vessel and its associated charter would achieve in a sale and purchase transaction between a willing buyer and willing seller.
The principle behind MVWC is to start with the open market value of the vessel alone. To this we add an estimate of the value of the charter, which we make by running two DCF calculations: one with the charter income included and one assuming the vessel trades spot. The difference between these is the DCF value of the charter (positive or negative) which we add to the vessel’s market value.
In a firm charter market, like in the first half of 2008, vessels with charter rates below the then-booming spot rate were sold at significant discounts to comparable charter-free vessels. In a weak spot market the opposite is also true. Our model accounts for such possibilities.
The calculation of MVWC contains the following steps.
Market Value of vessel
The charter-free Market Value of the vessel is calculated using our well-established MV model.
DCF values of vessel with and without charter
Our automated DCF model makes short and long-term projections of the vessel’s future earnings from average historical charter rates. The short-term projection is derived from the average rate over the last three months of earnings in the vessel’s market sector, while the long-term is derived from the average rate over the last 15 years. The vessel’s projected future earnings start at the short-term rate and change to the long-term rate over three years.
For more details of our DCF model, please refer to the full DCF methodology.
The model enables the default projected earnings to be overwritten with fixed charter earnings, where these are known, as shown in Figure 1. When MVWC is calculated this fixed rate is used.
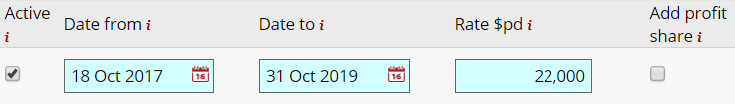
Figure 1. Showing an example of when Market Value with Charter is calculated using charter information
The default model computes the discounted cash flow over the remaining useful life of the vessel but this can be customized by inputting an earlier stop date. In the case of MVWC, the end date for the charter is automatically used as the stop date.
This allows us to calculate two DCF values:
DCF Value with Charter, using the known fixed charter rate and the cash flow over the period of the charter.
DCF Value without Charter, using the default projected charter rate and the cash flow over the same period of the charter.
Charter value
We estimate the value of the charter as the difference between these two DCF values:
Charter Value = DCF value of vessel with charter – DCF value of vessel
Note that the charter value will be positive if the charter earnings exceed the projected earnings and negative if they are less.
Market Value with Charter
We obtain the MVWC by adding the charter value to the market value of the vessel:
Market Value with Charter = Market Value + Charter Value
This results in a premium if the charter value is positive, and a discount if negative.
