IMOS - Fuel/Lube Types
On the Fuel/Lube Types form, you can specify the fuel, lubricant, and oil types used on the Vessel, Tow, Boat, Barge, Fuel Zones, and other forms.
On the Data Center menu …, under Vessels, click Fuel/Lube Types.
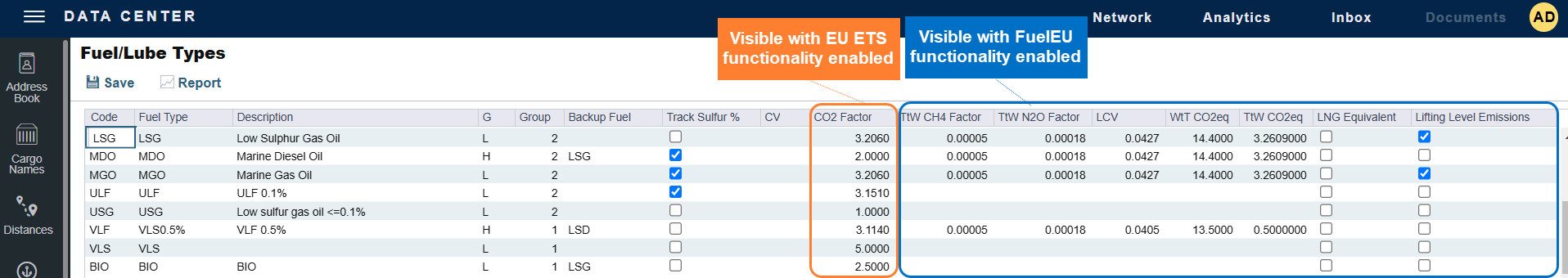
Depending on the Sustainability features you have enabled in IMOS, you may see the additional columns shown in the following image.
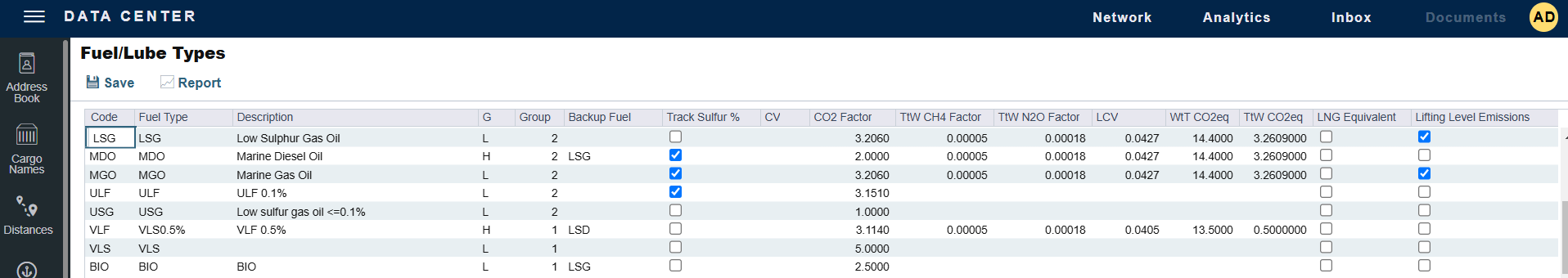
Code: short name for type of fuel or lubricant, limit of 3 characters.
Fuel Type: full fuel or lubricant name.
Description: free-form text field for a brief description of the fuel or lubricant type.
G: fuel grade.
G = General Purpose (can be used as either low or high sulfur fuel)
H = High Sulfur
L = Low Sulfur (can be selected for ECA Fuel Zones)
Group: a number used to group High and Low Sulfur fuel types to be consumed for the same purpose – calculating CP consumption. 2 fuel types (HS and LS) in the same group cannot both be burned at the same time. The relation between the 2 fuel types’ CP consumption is called the relation between the 2 fuel types’ actual consumption.
Backup Fuel: fuel type to use as a backup to estimate consumption when a vessel is estimated to run out of the Fuel Type. If a vessel is estimated to run out of the Backup Fuel type of does not have it on board, the Backup Fuel’s backup is used.
Track Sulfur %: Select to track sulfur percentage. Veslink can gather information on the sulfur content of fuel ROBs, facilitating compliance with the Green Marine initiative.
CV: Calorific Value, in MMBTU/m3. Used in LNG pricing in the voyage for LNG fuel types only.
CO2 Factor: represents the Tank to Wake CO2 Emissions Factor, which is the tons of CO2 emitted per ton of fuel consumed.
TtW CH4 Factor: Tank to Wake methane (CH4) emission factor.
TtW N2O Factor: Tank to Wake nitrous oxide (N2O) emission factor.
LCV: Lower Calorific Value expressed in MJ/g.
WtT CO2eq: Well to Tank CO2 equivalent emissions.
TtW CO2eq: Tank to Wake CO2 equivalent emissions.
LNG Equivalent: This checkbox is used for accurate FuelEU calculations and does not drive any other logic.
The "LNG Equivalent" checkbox should only be applied to the fuel type “LNG."
Upon checking this for LNG fuel, IMOS will apply the published EU Cslip factor based on the engine type of a vessel.
For this to work, the engine type must be set up on the LNG vessel. To do this, navigate to Data Center > Vessel > Details Tab, specify the engine type in the “Engine Make/Type” field, and then save.
Using the Lifting Level Emissions column to capture fuel emissions factors in the Bunker Purchase form
To capture fuel emissions factors in the Bunker Purchase form, select the box in the Lifting Level Emissions column for each fuel type. The form will then display these fuel types.
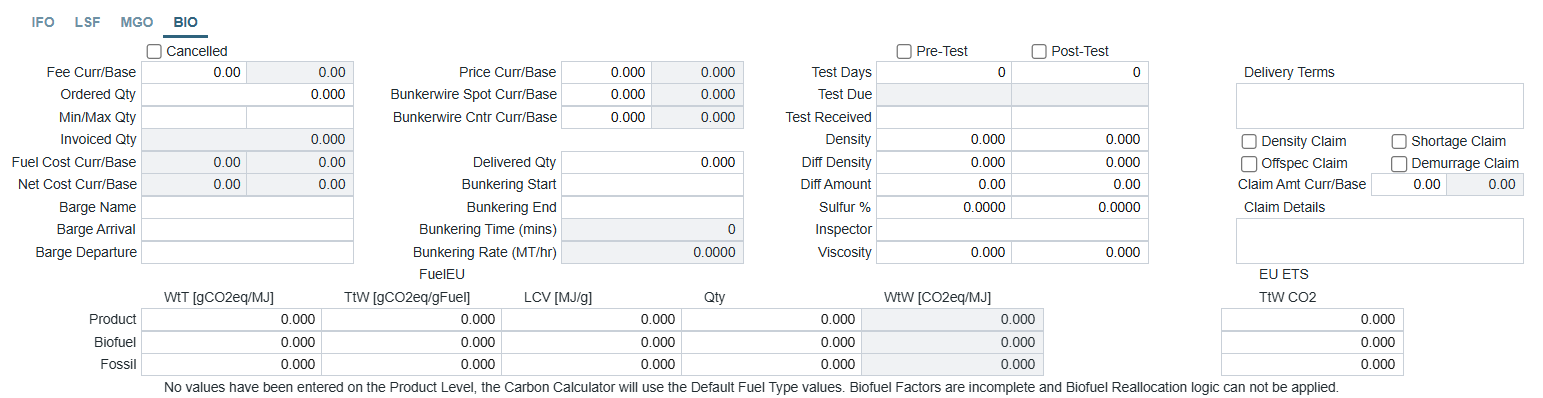
The fuel tab of the Bunker Purchase form. Fuel emissions factors are included at the bottom.
Additional notes beyond the field help:
G: Low-sulfur Fuel/Lube Types (marked L in this column) appear on the Fuel Zones form, where estimated/projected low-sulfur consumption can be specified for different ECA Fuel Zones.
If a fuel's CO2 Factor is ≤ 1.0000 or empty, the CO2 (MT) column in the Estimate, Speed Comparison Analysis, and Voyage Manager will not calculate and will appear light red.
To disable Backup Fuel types, select the Disable Backup Fuels check box on the Bunker Planning and Voyage Bunkers forms.
If only one fuel type has an IGS consumption rate specified for a vessel, this type is always used for IGS consumption in the Estimate/voyage, regardless of the Misc. Consumption settings on the Fuel Zones form.
G: General sulfur Fuel/Lube Types (marked G in this column) will continuously consume throughout the voyage with other fuel types (such as L and H).
Fuel Types cannot be deleted once they are in use; this is to protect the integrity of the data for past voyages.
With a schema upgrade to version 46.3, a new checkbox column labeled LNG Equivalent appears on the Fuel/Lube Types form. The Engine Make field on the Vessel Details tab becomes Engine Make/Type and includes an additional dropdown menu with options for various LNG and LBSI engine types.
CP Consumption for Grouped Fuels
On this form, you can group High and Low Sulfur fuel types to be consumed for the same purpose. Having two fuel types (HS and LS) in the same group means that the vessel cannot burn both fuel types at the same time.
The example above shows two fuel Groups defined. IFO and LSF belong to one group; LSG and MGO belong to another. Therefore, the vessel cannot consume IFO at the same time as LSF. The same applies to LSG and MGO.
